Discover solar energy options for homes and small businesses in Indonesia
Introduction to Solar Energy in Indonesia
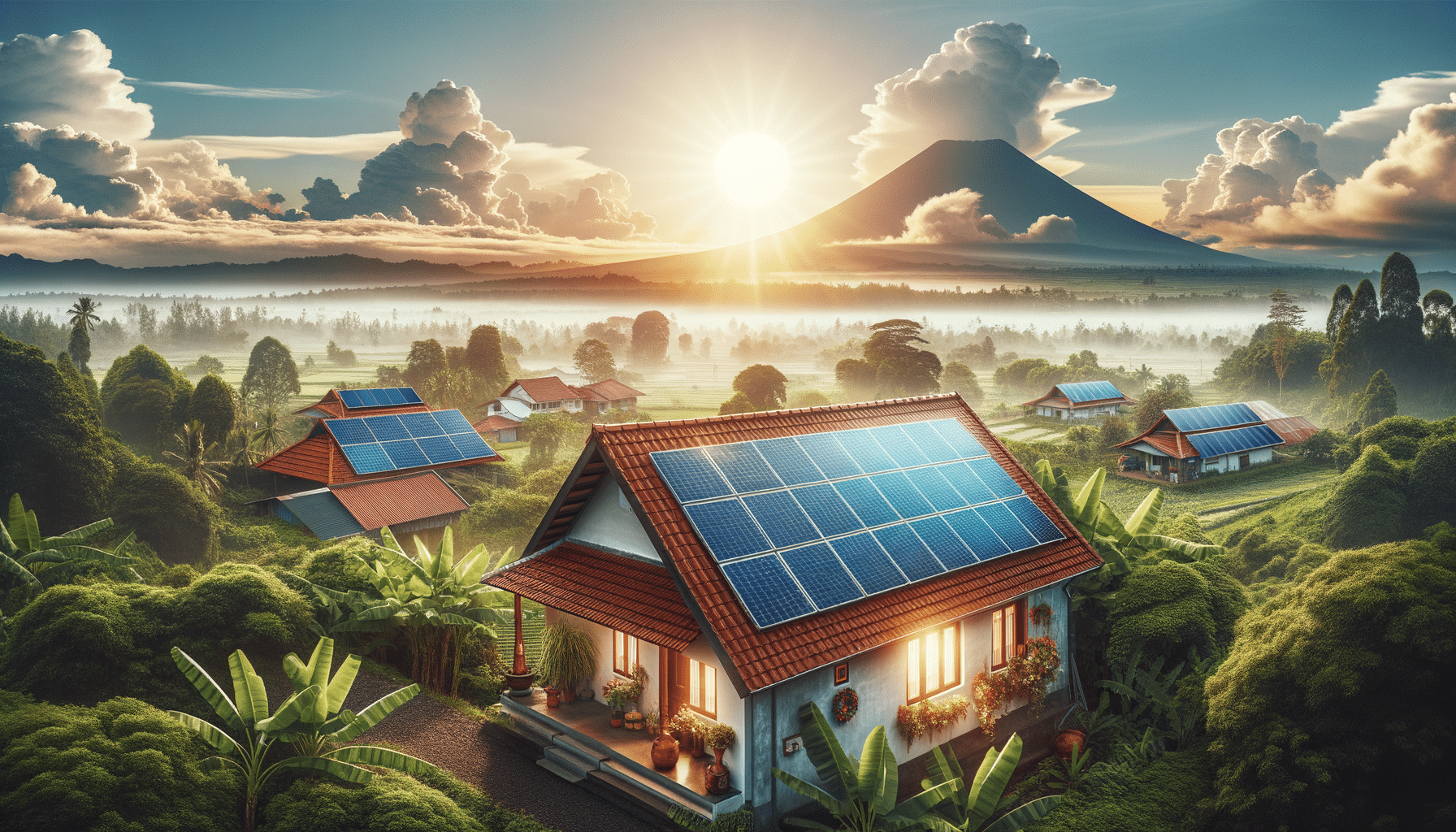
As the world moves towards sustainable energy solutions, solar energy has emerged as a prominent option for reducing carbon footprints and promoting environmental sustainability. In Indonesia, a country blessed with abundant sunlight, solar energy systems have gained significant attention for both residential and commercial applications. The adoption of solar panels not only contributes to environmental conservation but also presents an opportunity for substantial energy savings, making it a viable choice for homes and small businesses.
Indonesia’s geographical position near the equator provides it with high solar irradiance, making it an ideal location for harnessing solar power. This potential has led to increased interest in solar energy systems, particularly for those looking to reduce dependency on conventional electricity sources and lower energy costs. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of solar energy systems, including their benefits, types, installation processes, and how they can be integrated into homes and small businesses in Indonesia.
Benefits of Solar Energy Systems
Solar energy systems offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive option for both individuals and businesses. One of the primary advantages is the potential for significant energy savings. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar panels can reduce or even eliminate electricity bills, providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional energy sources.
Additionally, solar energy is a renewable resource, which means it is inexhaustible and environmentally friendly. Utilizing solar power helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and decreases reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future. Moreover, solar panels require minimal maintenance, making them a convenient and long-term investment.
For small businesses in Indonesia, adopting solar energy can enhance their brand image by showcasing a commitment to sustainability. This can attract environmentally conscious customers and partners, providing a competitive edge in the market. Furthermore, government incentives and subsidies for solar installations can reduce the initial investment costs, making it more accessible for a wider audience.
Types of Solar Panels and Systems
When considering solar energy systems, it’s essential to understand the different types of solar panels and configurations available. The most common types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages.
- Monocrystalline Panels: Known for their high efficiency and longevity, monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal structure. They are ideal for areas with limited space as they provide more power output per square meter.
- Polycrystalline Panels: These panels are made from multiple silicon crystals, making them less expensive but slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels. They are a popular choice for residential installations due to their cost-effectiveness.
- Thin-Film Panels: Lightweight and flexible, thin-film panels are suitable for large-scale installations. They perform well in low-light conditions, but their efficiency is generally lower compared to crystalline panels.
In addition to panel types, solar systems can be categorized into grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems. Grid-tied systems are connected to the local electricity grid, allowing users to sell excess power back to the grid. Off-grid systems operate independently, providing power in remote areas without access to the grid. Hybrid systems combine features of both, offering flexibility and backup power during outages.
Installation Process and Considerations
The installation of solar panels involves several steps and considerations to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. The process begins with a site assessment to determine the suitability of the location and the amount of sunlight it receives. This assessment helps in designing a system that meets the specific energy needs of the home or business.
Once the design is finalized, the installation process involves mounting the panels on rooftops or ground structures, connecting them to inverters, and integrating them with the existing electrical system. It’s crucial to hire experienced and licensed installation providers to ensure the system is installed correctly and safely.
Several factors should be considered during installation, including the orientation and tilt of the panels, shading from nearby structures, and local regulations. Proper orientation and tilt maximize sunlight exposure, while minimizing shading ensures maximum energy production. Additionally, compliance with local building codes and obtaining necessary permits are essential to avoid legal issues and ensure the system’s longevity.
Potential Energy Savings and Return on Investment
Investing in solar energy systems can lead to substantial energy savings and a favorable return on investment over time. The initial cost of installation can be offset by the reduced electricity bills, and in some cases, users may even receive compensation for excess energy fed back into the grid.
The payback period for solar installations in Indonesia typically ranges from 5 to 10 years, depending on the system size, energy consumption, and available incentives. After the payback period, the energy generated is essentially free, providing long-term financial benefits.
Furthermore, the increasing cost of conventional energy sources makes solar energy a more attractive option. As technology advances and production costs decrease, solar panels are becoming more affordable, increasing accessibility for a broader audience. For small businesses, the savings on energy costs can be redirected towards growth and development, enhancing profitability.
In conclusion, solar energy systems offer a sustainable and economically viable solution for homes and small businesses in Indonesia. By harnessing the abundant sunlight, individuals and businesses can reduce their environmental impact, enjoy energy savings, and contribute to a cleaner future.